Electricity powers our modern lives, from the moment we wake up to the moment we go to bed. In this article, we will dive into the world of household electricity, exploring its generation, distribution, safety, and energy-efficient practices for a more sustainable future.

The Basics of Household Electricity
- Generation: Electricity is generated from various sources, including fossil fuels, nuclear power, hydroelectric dams, wind turbines, and solar panels. It’s then transmitted to homes through power lines.
- Distribution: Power lines deliver electricity to substations, which step down the voltage for safe distribution to residential areas. Transformers further reduce voltage for household use.
- Voltage and Current: Household electricity typically operates at 120 volts in the United States and 230 volts in many other countries. The flow of electricity is measured in amperes (amps).
Electrical Safety in the Home:
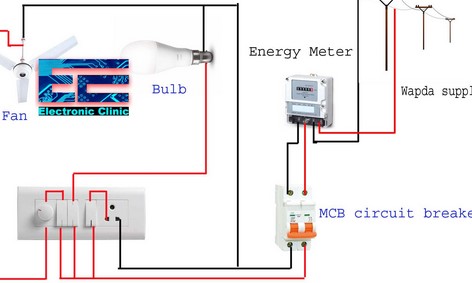
Electrical Panel:
The electrical panel, also known as a breaker box, distributes electricity throughout the house. Circuit breakers or fuses protect against electrical overloads.
Outlets and Wiring:
Regularly inspect outlets and wiring for signs of wear, damage, or overheating. Replace damaged components promptly to prevent electrical fires.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs):
GFCIs are essential in wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens. They shut off power in case of a ground fault, reducing the risk of electrocution.
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs):
AFCIs detect and prevent electrical fires caused by arcing or sparking in wiring. They are often required in bedrooms and living areas.
Energy Efficiency at Home:
LED Lighting:
Replace incandescent bulbs with energy-efficient LED lights to reduce electricity consumption and lower your energy bills.
Appliance Efficiency:
Look for ENERGY STAR-rated appliances that are designed to consume less energy. Unplug or power off devices when not in use to prevent standby power consumption.
Insulation and Weatherization:
Properly insulate your home and seal gaps and cracks to reduce heating and cooling energy waste.
Smart Thermostats:
Install a programmable or smart thermostat to optimize your heating and cooling systems, saving energy without sacrificing comfort.
Renewable Energy Options:
- Solar Panels: Solar photovoltaic panels allow homeowners to generate their electricity from the sun’s energy, reducing reliance on grid electricity and lowering bills.
- Wind Turbines: In suitable areas, residential wind turbines can harness wind energy to generate electricity for homes.
- Geothermal Systems: Geothermal heat pumps use the stable temperature of the Earth to heat and cool homes efficiently.
Backup Power Solutions:
- Generators: Standby or portable generators provide backup power during blackouts, ensuring essential appliances and systems remain functional.
- Battery Storage: Home battery storage systems store excess energy generated from solar panels, providing power during outages and reducing reliance on the grid.
The Future of Household Electricity:
- Decentralization: Distributed energy resources, such as solar panels and residential battery storage, are leading to a more decentralized grid, allowing homeowners to produce and store their electricity.
- Grid Modernization: Smart grids, equipped with advanced sensors and controls, are becoming more widespread, enhancing grid reliability and efficiency.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): As EV adoption grows, homes equipped with EV charging stations are becoming increasingly common, further integrating electricity into daily life.
Conclusion
Household electricity is the lifeblood of modern homes, powering everything from lights to appliances and heating. By understanding its basics, practicing safety measures, and embracing energy-efficient practices and renewable technologies, homeowners can not only reduce energy costs but also contribute to a more sustainable and resilient energy future. As we continue to innovate and adapt to new technologies, the world of household electricity promises exciting developments and opportunities for a greener tomorrow.